The first comprehensive benchmark for Kubernetes LLMs
KubeBench is a domain-specific benchmark that scores LLMs on production-grade Kubernetes tasks across 810 carefully designed scenarios and the eight core resource types that power real clusters, from RBAC and namespaces to secrets and workloads.
What KubeBench measures
Instead of grading YAML by string similarity, KubeBench evaluates how models behave against a live Kubernetes API.
- Real production tasks. Each prompt reflects a concrete cluster scenario, such as configuring quotas for a team namespace or tightening RBAC for a service account.
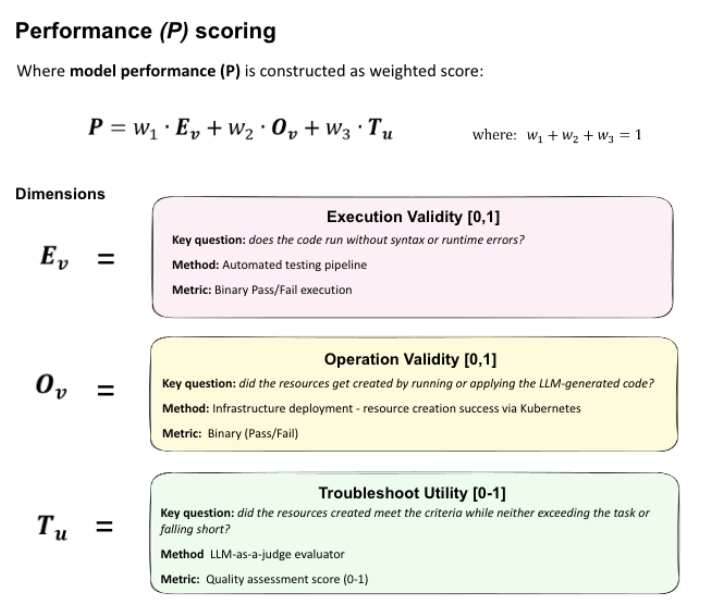
- Three-dimensional scoring. Models are evaluated on whether manifests parse, deploy, and actually satisfy the operational intent.
- Difficulty tiers. Tasks span easy, intermediate, and advanced levels to mirror day-to-day infrastructure engineering work.
- LLM-as-judge reasoning. A judge model inspects cluster state and explains whether the produced YAML truly fulfills the task rather than just “working by accident.”
Evaluation pipeline
For each task, the model generates Kubernetes YAML which is then validated against actual clusters (tested on both local Minikube and GKE Autopilot).
- 1. Execution validity. Does the control plane accept the manifest without syntax or runtime errors?
- 2. Operation validity. After applying the YAML, do all expected resources exist in the cluster with the right kinds and fields?
- 3. Troubleshooting & reasoning. A separate LLM judge reviews the live cluster JSON, original task, and response to score how well the solution covers requirements, avoids scope creep, and follows Kubernetes best practices.
At a high level, KubeBench summarizes model performance as a weighted combination of execution, operational behavior, and troubleshooting quality, giving infrastructure teams a single, interpretable signal while keeping the underlying dimensions available for deeper analysis.
Why this matters
Kubernetes adoption continues to grow across finance, healthcare, telecom, retail, and manufacturing, and thousands of engineers now depend on LLMs to generate, review, and troubleshoot manifests safely. Traditional text benchmarks ignore the declarative, order-independent nature of Kubernetes YAML and often punish functionally equivalent configurations.
KubeBench closes this gap by grounding evaluation in the only thing that really matters for infrastructure teams: how code behaves when it hits the cluster.
Full technical report
Dive into the full experimental setup, scoring framework, and model comparisons in the KubeBench technical report.
Implementation demo: Fine-tuning pipeline
Explore an end-to-end walkthrough of our Kubernetes fine-tuning pipeline, including dataset construction, noise filtering, annotation, and evaluation. This document complements KubeBench by showing how domain-specific performance is achieved in practice.
- Real-world Kubernetes training data sourcing
- Noise removal and dataset refinement
- Instruction-style task annotation with LLMs
- Complexity tiers and curriculum design
- Empirical effects of data quality on model behavior